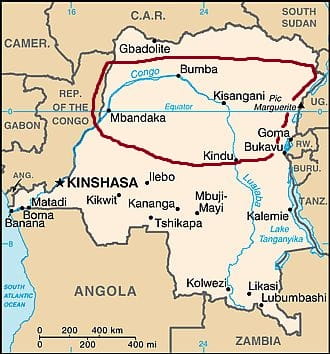
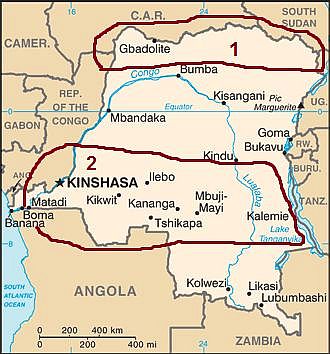
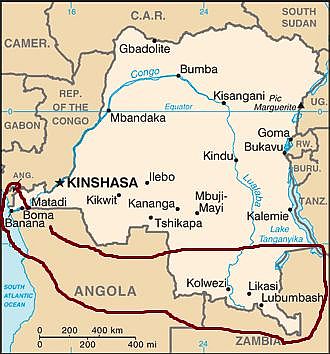
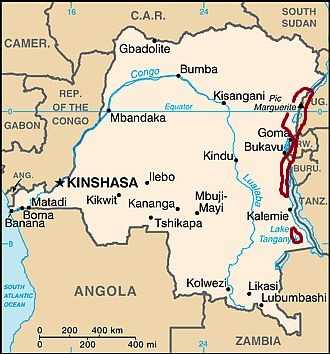
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has a very interesting mix of topography. The land goes from mountains near 8000 feet in the far east to the coast that falls into the sea. The country has two main watersheds, the Zaire and the Ogooue, which are separated by the savanna of the Plateau region. This Plateau region is one of four topographical region that divide the country, the rest of which are the Coastal region, the Escarpment region and the Northeastern region. The Plateau region is located centrally in the country and has a rough elevation of 3000 feet. South of the Plateau region is the Escarpment region which is distinguished by long narrow furrows stretching parallel with each other out towards lower elevation. These furrows are almost entirely forested and stand between 2000 and 3000 feet in elevation. The Coastal region is tucked away in the south west corner of the country aptly on the coast. This region consists of mostly low lying treeless plains with occasional spurts from the Escarpment region. Finally there is the Northeastern region which consists primarily of swampland and stand about 1500 to 1600 feet in elevation. This region is a major flood zone because of the numerous tributaries that run through it and the low elevation. If you can picture the flow of this land it may look just as diverse as the ecology of it jungle.
The Democratic Republic of the Congo has a very interesting mix of topography. The land goes from mountains near 8000 feet in the far east to the coast that falls into the sea. The country has two main watersheds, the Zaire and the Ogooue, which are separated by the savanna of the Plateau region. This Plateau region is one of four topographical region that divide the country, the rest of which are the Coastal region, the Escarpment region and the Northeastern region. The Plateau region is located centrally in the country and has a rough elevation of 3000 feet. South of the Plateau region is the Escarpment region which is distinguished by long narrow furrows stretching parallel with each other out towards lower elevation. These furrows are almost entirely forested and stand between 2000 and 3000 feet in elevation. The Coastal region is tucked away in the south west corner of the country aptly on the coast. This region consists of mostly low lying treeless plains with occasional spurts from the Escarpment region. Finally there is the Northeastern region which consists primarily of swampland and stand about 1500 to 1600 feet in elevation. This region is a major flood zone because of the numerous tributaries that run through it and the low elevation. If you can picture the flow of this land it may look just as diverse as the ecology of it jungle.
"Congo, Republic of the (ROC) - Topography." Encyclopedia of the Nations. N.p., n.d. Web. 19 Apr. 2017.